Plain Bearing PV
Notes & Use
Calculates design values (velocity, force, and combined) of plain bearings when the following are true:
- For radial (journal) applications
- the bearing rotates around a shaft,
- the rotational motion is continuous (as opposed to an ocillating),
- the load is applied perpidicular to the axis of rotation (radial).
- For thrust applications:
- the load rotates upon the bearing, around a fixed center point,
- the thrust bearing’s bearing surface is circular or annular,
- the rotational motion is continuous,
- the load is applied parallel to the axis of rotation,
- the load is uniform across the surface area of the bearing.
This calculator does not address any issues beyond P, V, and PV calculations, such as:
- Effects of friction,
- Additional heat and energy-dispersal concerns,
- Dimensional changes due to heat deformation,
- Tribology/lubrication concerns,
- including cleanliness and suitability of lubricants
- Wear factors
- Operating Temperatures
- Lifetime calculations
- Shock-load and impact factors
Calcuations
Radial Figure
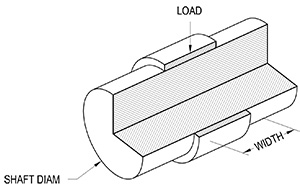
Radial Terms
$L$ = load on bearing, pounds force
$n$ = Shaft speed, rotations per minute
$d$ = Diameter of shaft (ID of bearing), inches
$w$ = Bearing width, inches
$P$ = Pressure on bearing, psi
$V$ = velocity of bearing surface, feet per minute
$PV$ = Pressure × Velocity
Radial Equations
$$ P_{actual} = \frac {L} {w d} $$
$$ V_{actual} = \frac {n d \pi} {12} $$
Thrust Figure

Thrust Terms
$L$ = load on bearing, pounds force
$n$ = Rotation speed, rotations per minute
$d$ = Inner diameter of bearing’s surface area, inches
$D$ = Outer diameter of bearing’s surface area, inches
$P$ = Pressure on bearing, psi
$V$ = velocity of bearing surface, feet per minute
$PV$ = Pressure × Velocity
Thrust Equation
$$ P_{actual} = \frac {4L} {\pi (D^2 - d^2)} $$
$$ V_{actual} = \frac {n \left( \frac{D - d}{4} \right) \pi} {12} $$
Pass/Fail Test
$P_{actual}$, $V_{actual}$, and $PV_{actual}$ are compared to the respective allowable values:
- Pass = actual < allowable
- Fail = actual ≥ allowable
Material P, V, and PV values
The design values provided by the drop-down material box are culled from various sources, notably Mcmaster-Carr and Wikipedia. A full table of those values is as follows:
| Material | P | V | PV |
|---|---|---|---|
| psi | fpm | psi×fpm | |
| SAE 841 | 2,000 | 1,200 | 50,000 |
| Graphite SAE 841 | 1,600 | 1,000 | 40,000 |
| SAE 660 | 4,000 | 750 | 75,000 |
| SAE 841 | 2,000 | 1,200 | 50,000 |
| SAE 863 | 4,000 | 225 | 35,000 |
| Nylon | 400 | 360 | 3,000 |
| Nylon MDS #1 | 2,000 | 393 | 3,400 |
| UHMWPE | 1,000 | 100 | 2,000 |
| Acetal | 1,000 | 1,000 | 2,700 |
| Ptfe | 500 | 100 | 1,000 |
| Ptfe (glass filled) | 1,000 | 400 | 11,000 |
| Rulon 641 | 1,000 | 400 | 10,000 |
| Rulon J | 750 | 400 | 7,500 |
| Rulon LR | 1,000 | 400 | 10,000 |
| Peek (blend 1) | 8,500 | 400 | 3,500 |
| Peek (blend 2) | 21,750 | 295 | 37,700 |
| Vespel | 4,900 | 3,000 | 30,0000 |
Sources
- Robert L. Mott, Machine Elements in Mechanical Design, 4th ed. pp. 669, 2003.
- Dupont Vespel Design Guide
- Mcmaster-Carr
- Wikipedia